
Efficient Financial Statement Prep for Small Businesses
Financial Statement Preparation for Small Businesses Best Practices and Tools
Financial statements are vital for small businesses. They provide insights into financial health and guide decision-making.
Understanding financial statement basics is crucial for business success. It helps in identifying areas for cost reduction and revenue growth.
This guide will explore best practices and tools for financial statement preparation for small businesses.
We'll cover essential financial reporting tips and small business accounting strategies.
By the end, you'll be equipped to prepare financials with confidence and clarity.
Why Financial Statements Matter for Small Businesses
Financial statements are crucial for understanding a business's financial position. They offer a snapshot of assets, liabilities, and equity.
These statements guide small business finance management. They help owners make informed decisions and craft effective strategies.
Reliable business financial reports are also essential for external stakeholders. Lenders and investors often require them to assess business viability.
Understanding and regularly updating financial statements helps owners track financial health. It fosters better budgeting and forecasting.
Key reasons why financial statements matter:
Assess financial health
Support decision-making
Fulfill lender and investor requirements
Facilitate budgeting and forecasting
Understanding the Basics: Key Financial Statements Explained
Understanding financial statement basics is essential for small business finance. These statements include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
Each serves a different purpose. They collectively give a comprehensive view of a business’s finances.
The balance sheet provides a snapshot at a given moment. It lists what the business owns and owes, along with the equity.
The income statement reflects a period's revenues and expenses, showing profit or loss. This helps in evaluating operational efficiency.
The cash flow statement reveals how cash moves in and out. It highlights liquidity and financial management.
Common elements of these statements include:
Assets
Liabilities
Equity
Revenues
Expenses
The Balance Sheet
A balance sheet presents a company's financial standing. It details assets, liabilities, and owners' equity at a specific time.
Assets are what the business owns. Liabilities denote what it owes to others.
Owner's equity represents the shareholder’s claim. It is pivotal for business financial reports.
Common components include:
Current and non-current assets
Current and non-current liabilities
Shareholders’ equity
The Income Statement
The income statement reveals profitability over a period. It lists revenues and expenses to show net profit or loss.
This statement helps in assessing business performance. It aids in strategic planning and operational tweaks.
Key parts to focus on:
Revenue
Cost of goods sold
Operating expenses
Net income
Understanding these figures helps in making informed decisions.

by Brett Jordan (https://unsplash.com/@brett_jordan)
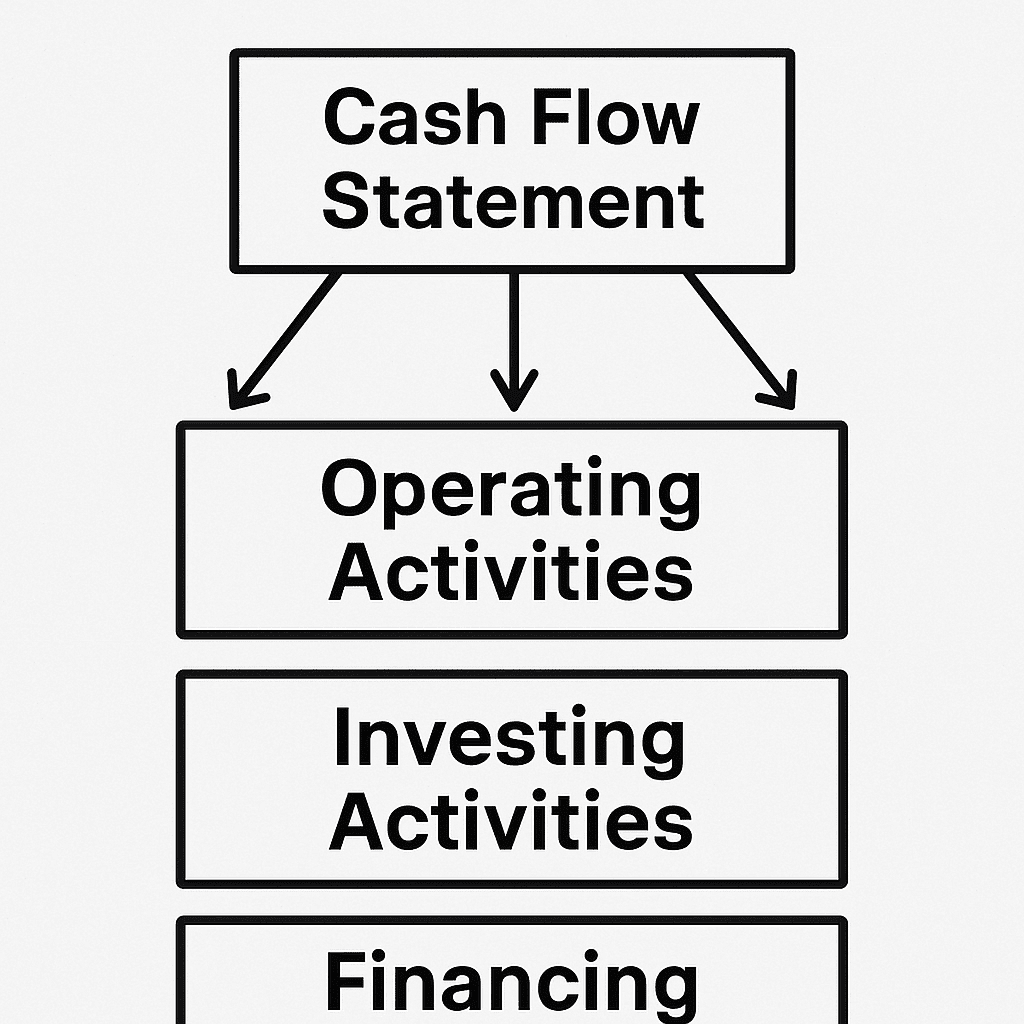
The Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks cash movement. It highlights a company’s liquidity by detailing inflows and outflows.
It comprises three sections: operating, investing, and financing activities. Each provides insights into cash usage.
Essential elements are:
Operating cash flow
Investing cash flow
Financing cash flow
This statement is vital for assessing a business's financial stability.
by Witchayaphon Suwanpakai (https://unsplash.com/@daemew)
Step-by-Step Guide to Financial Statement Preparation for Small Businesses
Preparing financial statements is a systematic process. Begin with accurate data collection and organization. Following specific steps ensures accuracy.
First, gather all financial records. Collect invoices, receipts, and bank statements.
Next, record all transactions. Reconcile them against your accounts to ensure consistency.
Prepare a trial balance. This step checks if your ledger accounts are balanced.
Adjust entries for accrued items. Review them for accuracy to prevent errors.
Construct your financial statements. Use the data to create meaningful reports.
Finally, conduct a comprehensive review. Distribute your financial statements to stakeholders.
1. Gather and Organize Financial Data
Start by assembling financial documents. Ensure you have everything needed to compile comprehensive reports.
Sort these documents into categories for ease. Important financial records include:
Receipts and invoices
Bank statements
Previous financial reports
This organization step is crucial. It sets the foundation for everything else.
2. Record and Reconcile Transactions
Next, accurately record each transaction. This requires entering data consistently.
Ensure all entries are correct by reconciling them with account statements. Important steps in this process include:
Entering transactions in the ledger
Verifying data against bank statements
Identifying discrepancies
This step maintains data accuracy, which is essential for further analysis.
3. Prepare the Trial Balance
A trial balance comes next in the process. It confirms that total debits equal total credits.
Prepare the trial balance by listing account balances. The main focus areas include:
Checking debit and credit alignment
Highlighting account imbalances
Correcting identified errors
This serves as a preliminary financial review.
4. Adjust Entries and Review for Accuracy
After preparing the trial balance, adjust entries. Ensure all financial information reflects current activities.
Conduct a thorough review to identify errors. Focus on:
Accruals and deferrals
Depreciation adjustments
Discrepancy corrections
This step guarantees the reliability of your data.
5. Construct the Financial Statements
Use the verified data to create financial statements. This includes preparing reports like the balance sheet.
Ensure all statements reflect accurate financial health. Key points to address are:
Finalizing the balance sheet
Completing the income statement
Drafting the cash flow statement
Each statement should communicate the company's financial standing.
6. Final Review and Distribution
Before distribution, review the statements thoroughly. Ensure clarity and accuracy to convey the right message.
Once reviewed, distribute them to stakeholders. Key actions include:
Conducting final audits
Ensuring compliance with standards
Sharing with investors and partners
This completes the preparation process for small business financial reporting.
Best Practices for Small Business Financial Reporting
Financial reporting is more than numbers. Adopt best practices to enhance the quality of your reports.
Consistency in reporting is vital. Use the same formats and accounting principles regularly to maintain clarity.
Accuracy cannot be overstated. Make sure every figure is correct to avoid misrepresentation.
Regular financial reviews can benefit your small business. Schedule reviews to keep financial insights up-to-date.
Consider these best practices for effective financial reporting:
Use clear and concise language
Integrate visuals for better understanding
Ensure compliance with accounting standards
Remember, these practices build trust with stakeholders. They also provide valuable insights into financial health.

by Ivan Shilov (https://unsplash.com/@mycreate)
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Financial Statement Preparation
Mistakes in financial statements can lead to poor decisions. Avoid these common errors in your preparation process.
One frequent mistake is overlooking data updates. Always use current information to ensure accuracy.
Also, pay attention to detail. Errors in numbers or notes can impact your entire report.
Watch out for these common mistakes:
Misclassification of accounts
Ignoring minor transactions
Overlooking adjustments
By avoiding these pitfalls, you will produce reliable financial statements. Proper preparation fosters better decision-making and maintains credibility with stakeholders.
Essential Tools and Software for Small Business Accounting
Software solutions simplify small business accounting. They automate tasks and reduce errors in bookkeeping and financial statement preparation.
These tools also offer real-time insights. Accessible financial data helps you make informed business decisions swiftly.
Consider using the following essential tools:
QuickBooks: User-friendly and comprehensive for small businesses
Xero: Ideal for cloud-based accounting
FreshBooks: Easy invoicing and expense tracking

by Sayan Majhi (https://unsplash.com/@minimalsayan)

by FIN (https://unsplash.com/@fin21)
Each tool provides unique features to support efficient financial management. Choose one that aligns with your business needs. Automated solutions ensure accuracy and save time, letting you focus on growing your business.
Financial Reporting Tips for Small Business Owners
Effective financial reporting requires attention and diligence. Regularly review your business financial reports to catch errors early.
Consider these tips to enhance your reporting practices:
Set a consistent reporting schedule
Align reports with business goals
Review financial statements for accuracy
Simplifying your processes can also lead to better insights. Use clear formats and straightforward language to ensure transparency.
By staying proactive, you can improve small business finance management. Your efforts will foster a better understanding of financial health and drive smart business decisions.
Leveraging Financial Statements for Better Business Decisions
Financial statements are powerful tools for business insight. They help uncover trends and patterns critical for strategic decisions.
Using these statements effectively enhances decision-making. Consider the following ways:
Compare performance against industry benchmarks
Identify cost-saving opportunities
Assess business growth potential
Analyzing these reports regularly can guide future strategies. With financial insights, you can align your operations with long-term objectives. Smart decisions today set the stage for a prosperous future.
Frequently Asked Questions About Financial Statement Preparation
What are the essential financial statements for small businesses?
Small businesses primarily focus on three statements: the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. Each serves a distinct purpose.
How often should financial statements be prepared?
Regular preparation is vital. Many businesses prepare these monthly, quarterly, and annually to ensure up-to-date information.
Why are accurate financial statements important?
Accurate reports provide insights into financial health. They help in making informed decisions and complying with regulations.
Where can small businesses find financial statement templates?
Numerous accounting software tools offer built-in templates. Additionally, online resources provide free templates catered to various needs.
Conclusion: Building a Strong Financial Foundation
Creating reliable financial statements is crucial for small businesses. Accurate reports lead to better strategic planning and effective financial management.
Engaging with financial statements regularly can aid in understanding business performance. This promotes transparency and accountability within the organization.
By following best practices and using appropriate tools, small businesses can establish a solid financial foundation. This foundation supports growth and long-term success.
Contacts
🌐 Website: gadzhieva.com
📧 Email: svetlana@gadzhieva.com
📱 Phone: (510) 974-3115
💬 Telegram: https://t.me/Svetlana_CPA
📸 Instagram: @gadzhievacpa
💼 LinkedIn: Svetlana Gadzhieva CPA